Blood sugar levels or glycaemia should be monitored during pregnancy. A fasting glucose test is carried out at the beginning of the pregnancy and an oral glucose load test in the later weeks. If diabetes is diagnosed, the pregnant woman must check her blood glucose level daily. What is the normal blood glucose level during pregnancy and how can it be measured?
Blood glucose levels during pregnancy – what is the correct blood glucose level?
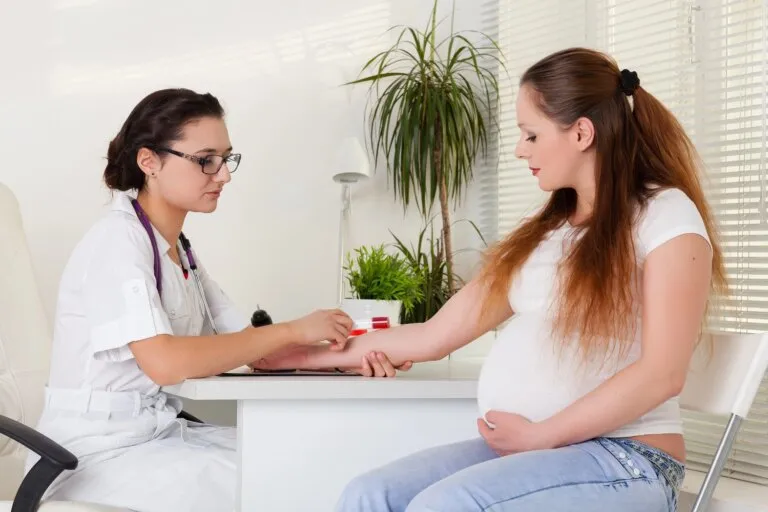
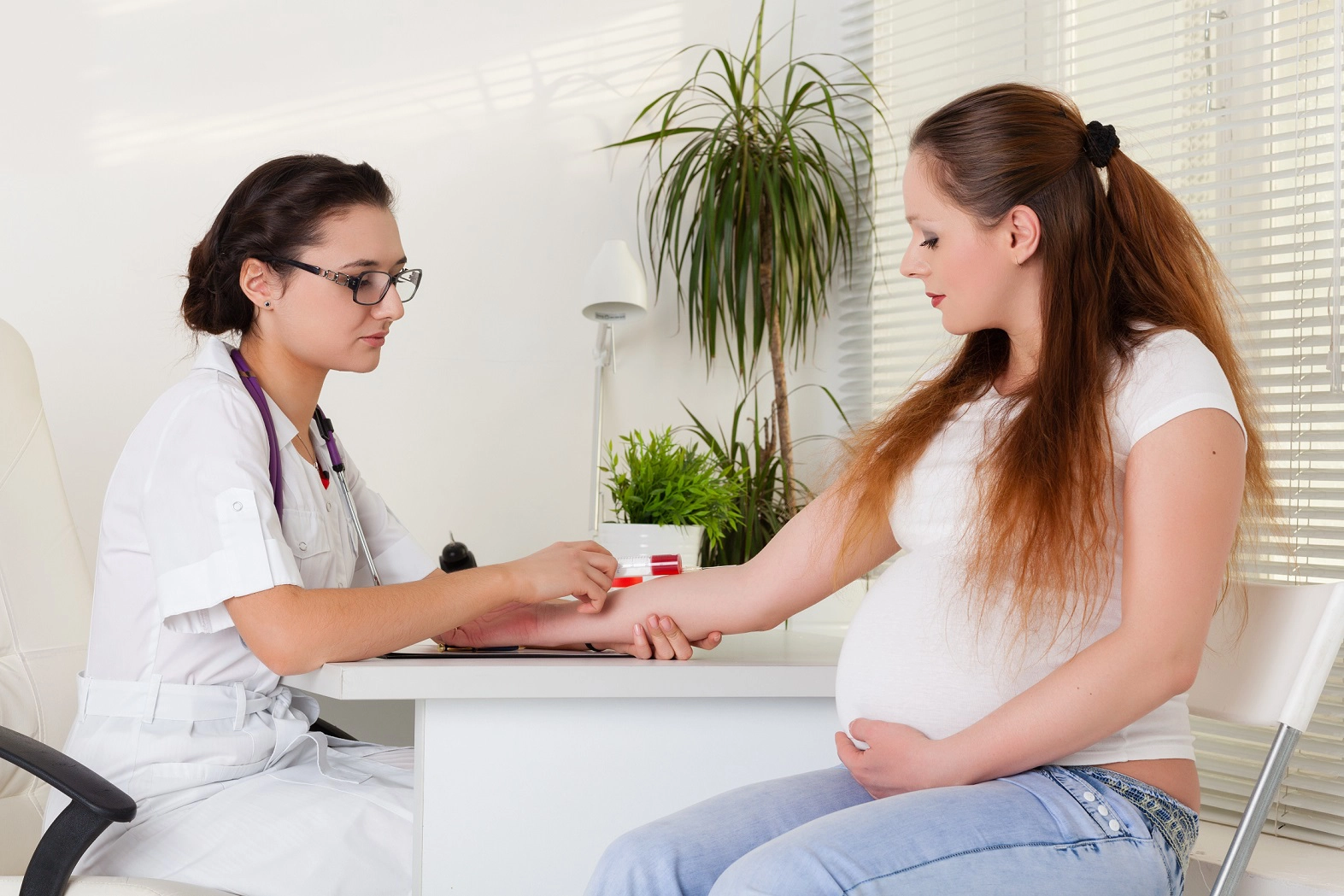
The blood glucose level during pregnancy is tested for the first time at the beginning of pregnancy. This is a fasting blood glucose test in which the blood glucose level should not exceed 92 mg%. If there are risk factors for gestational diabetes, such as being overweight, having a high birth weight or being over 35 years of age, the expectant mother should also carry out an oral glucose load test at the beginning of the pregnancy, in which the fasting glucose is measured and then one and two hours after drinking a 75 g glucose solution.
The blood glucose level in the OGTT test (oral glucose tolerance test) is considered normal during pregnancy:
- On an empty stomach: less than 92 mg/dl (<5.1 mmol/l)
- After 60 minutes: less than 180 mg/dl ( <10.0 mmol/l)
- After 120 minutes: less than 153 mg/dl ( ≤8.5 mmol/l)
When is blood glucose measured during pregnancy?
Blood glucose levels during pregnancy should be measured on an empty stomach and one hour after the main meals if diabetes is present. It is also advisable to check your blood sugar regularly at night between 2am and 4am. The expectant mother should be equipped with her own blood glucose meter and measuring strips. It is also possible to wear a special sensor that can be used to measure blood glucose continuously during pregnancy and does not require multiple pricks.
Abnormal blood sugar levels during pregnancy – treatment
If the fasting blood glucose test is abnormal, an oral glucose load test is recommended. Diabetes is diagnosed if the blood glucose values in the OGTT are abnormal. A distinction is made between diabetes during pregnancy and diabetes before pregnancy. Treatment is initially carried out with a diet. If this is ineffective and the blood glucose values at home are abnormal, insulin therapy is initiated. The decision on the treatment of gestational diabetes is made by the treating doctor or diabetologist. Pregnancy complicated by abnormal blood glucose levels is associated with complications and therefore requires special care.
Continuous measurement of blood glucose levels during pregnancy
Many expectant mothers complain about having to measure their blood glucose several times with a blood glucose meter. A special kit for continuous blood glucose monitoring with a sensor on the arm has recently become available for pregnant women. This allows blood glucose trends to be recognised and night-time measurements provide information on the effectiveness of diabetes treatment during the day.
Abnormal sugar levels during pregnancy – complications
Poorly controlled gestational diabetes can lead to a number of complications for both the child and the mother. It can lead to excessive foetal growth, macrosomia and subsequently to shoulder dystocia at birth. The risk of growth abnormalities is greater with gestational diabetes, which is why more frequent ultrasound and ECG checks of the baby are required. According to the recommendations, the birth should take place after the 38th week in the case of gestational diabetes and after the 39th week in the case of gestational diabetes.